- READ MORE: NASA video captures a new perspective on the "city-destroying" asteroid
Unless you've been living in complete isolation, you're probably aware of the asteroid that poses a significant threat to humanity, often referred to as a "city-killer."
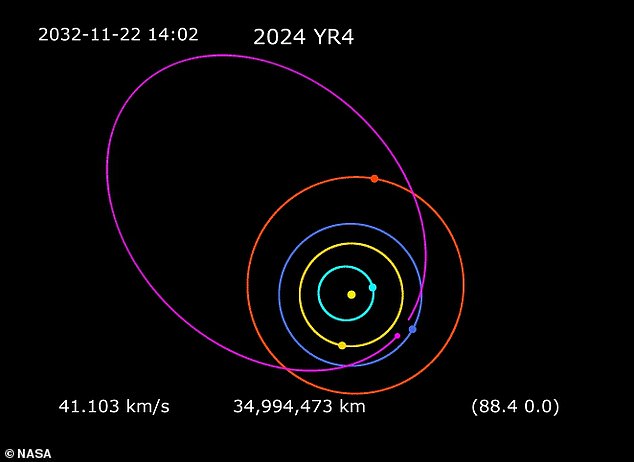
The asteroid 2024 YR4, which was discovered in December, is estimated to be approximately 130 to 300 feet (40 to 90 metres) in diameter.
's Big Ben.
The space rock's latest estimates
.
The news about the potential impact is still 7.5 years away, but it has already generated widespread concerns around the globe about the very real possibility of a devastating impact.
save us?
MailOnline's Science and Technology Editor, Shivali Best, responds to your inquiries regarding asteroid 2024 YR4.


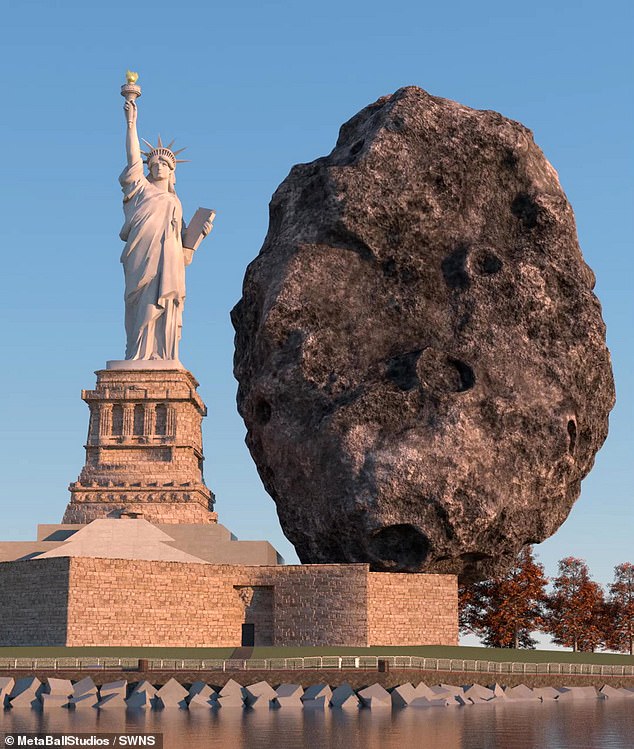
What is the size of the asteroid?
The estimated diameter for 2024 YR4 is approximately 130 to 300 feet (40 to 90 meters).
At the lower end of this estimate, the asteroid would be approximately three-fourths the height of Nelson's Column.
's Big Ben.
Where could it hit?
scientist has predicted exactly
David Rankin, an engineer with the NASA-funded Catalina Sky Survey Project, has outlined the 'risk corridor' based on the asteroid's current trajectory.
.
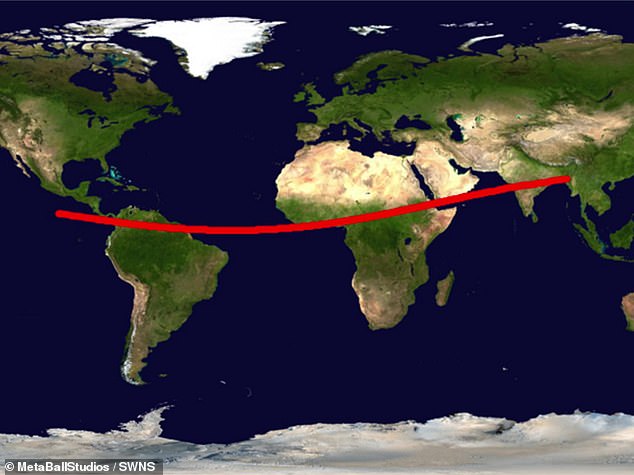
Worryingly, this path stretches across eight of the world's 100 most densely populated cities, including Bogota, Abidjan, Lagos, Khartoum, Mumbai, Kolkata, and Dhaka.
What kind of devastation would occur if it were to strike the center of a metropolitan area?
If the asteroid hits Earth, it would cause a blast equivalent to detonating 7.7 megatons of TNT, resulting in a crater approximately 3,000 feet in diameter.
Alternatively, instead of impacting Earth's surface, 2024 YR4 may explode in mid-air in what is referred to as an 'airburst'.
The airburst from the asteroid could potentially cause widespread destruction, resulting in the collapse of buildings and shattered windows across an entire city, depending on the asteroid's size.
If the asteroid were to explode over the ocean, NASA states that it would be unlikely to trigger a substantial tsunami, whether it occurs in the middle of the ocean or closer to the shore.
What's the likelihood that scientists may have made an error?
Since the asteroid was initially spotted in December, its projected likelihood of impacting Earth has undergone multiple revisions.
It's not surprising that many people are questioning whether the US space agency has made a mistake.
Currently, there is limited information available about its size and orbital path.
As NASA collects additional observations of the asteroid over the next 7.5 years, its future path will become more clearly defined, enabling a more accurate assessment of our situation.
What are the probabilities of this event actually occurring?
According to NASA's latest estimates, there is a one-in-67 (or 1.5%) likelihood that the asteroid will impact Earth on December 22nd, 2032.
The asteroid is currently moving away from Earth, and by April, it will be at such a great distance that it will no longer be visible from Earth-based telescopes.
The next time it will be bright enough to detect will be in 2028.
What factors are contributing to the increasing likelihood of a particular outcome?

The likelihood of the asteroid colliding with Earth has decreased this week from 3.1% to 1.5%.
NASA forecasts that, as additional data is gathered, this likelihood will likely decrease to 0.
Does NASA have the capability to deviate from its planned course of action?
In 2022, NASA's DART mission tested whether it's feasible to divert an asteroid by crashing a spacecraft into it.
Although that mission was a success, it is unlikely that the same method can be applied to this asteroid.
Researchers claim it takes a minimum of 10 years to plan, build, and carry out an asteroid deflection mission, leaving NASA insufficient time before the predicted 2032 collision.
The tweet says: "So much could go wrong if we try to hit it with something like DART."
Most asteroids are not solid rocks, but rather "rubble piles" – clusters of loose boulders, stones, and sand that are held together by the relatively weak gravitational forces of space.

We currently lack information on the exact size of 2024 YR4, or even whether it's a rubble pile asteroid. However, colliding a spacecraft like DART with a rubble pile asteroid could potentially produce a cloud of debris that could still head towards Earth.
"No one wants to unintentionally 'disrupt' an asteroid, as it's possible that its fragments could still be on a collision course with Earth," Dr. Andrews stated.
Will a nuclear device be required?
One of the most frequently discussed methods is employing a nuclear weapon to obliterate the asteroid.
However, NASA says this would not occur as depicted in the movie Armageddon, where a hole was drilled into the asteroid and a nuclear bomb was detonated.
Speaking in 2019, Lindley Johnson, NASA's planetary defense officer, said: 'If you've seen those movies, they're completely misleading.
'That's not how we would utilize a nuclear explosive device to achieve this outcome in the slightest.'
Detonating a nuclear weapon on or within an asteroid could potentially create more issues for us by launching multiple smaller space rocks into our path.
According to NASA, the most effective approach would be to detonate a nuclear weapon a few hundred meters away from the asteroid.
"That leads to an intense heating of the surface of the asteroid on that side, causing it to become extremely hot, and the surface material will then vaporize and be expelled from the asteroid," Johnson explained.
The dramatic action would result in an equal and opposite reaction, causing the asteroid to rebound away from Earth.
Currently, nuclear weapons are not authorized for use in space.
Article IV of the Outer Space Treaty prohibits nuclear or mass destruction weapons in Earth's orbit, on celestial bodies, and in outer space.
Do I need to go to work on that particular day?
It might be a bit early to request a day off from your supervisor.
But if it ultimately turns out that the asteroid is headed straight for your hometown, I wouldn't be surprised if you'd be eager to book the next available flight out of there!

Can Elon Musk be our savior?
Elon Musk is well-known for his unconventional and eccentric concepts, as seen in products such as Tesla's non-traditional pants and The Boring Company's flamethrowers.
But if the asteroid were to head our way, it could be SpaceX, his company, that comes to the rescue.
In response to a user on X, Musk stated that SpaceX's super-heavy Starship rockets could be 'ideal' for safeguarding Earth.
"Spacecraft stationed on Mars or even more effectively, scattered throughout the asteroid belt, would be perfect for safeguarding Earth from asteroids and particularly comets," he tweeted.
Read more