.
The nearly 200-foot-wide asteroid, designated 2024 YR4, has a 1.2 percent probability of impacting Earth on December 22, 2032.
This makes it especially important to pay attention to the potential impact it could have, especially if it were to occur in a densely populated area like a major city.
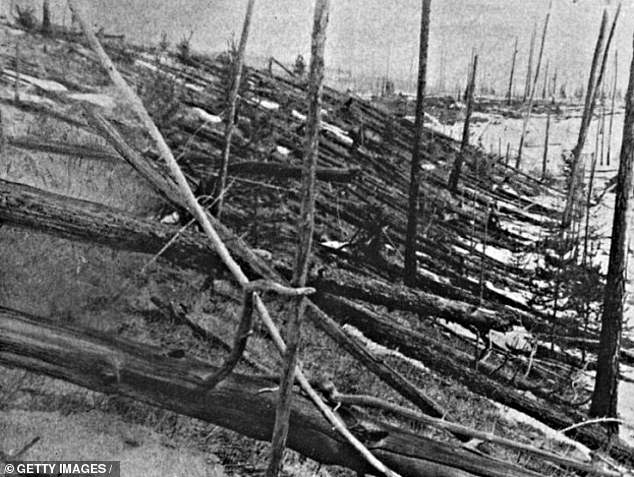
When it burst through Earth's atmosphere in 1908, causing the deaths of three people.
The explosion erupted in the sky over Siberia in a sudden 'air burst,' unleashing a force equivalent to the detonation of 50 million tons of TNT and devastating approximately 80 million trees over an area of 830 square miles of forest.
On December 22, 2032, the asteroid will approach within a distance of approximately 66,000 miles from our planet.
There is a possibility that orbital uncertainties could elevate the risk of the object colliding directly with Earth from a one percent chance to approximately 1.2 percent.
The automated Sentry risk list, which ranks recognized Near Earth Objects (NEOs) according to how likely they are to collide with our planet.

Wiping out entire human communities in the affected area.
However, the likelihood of this asteroid impacting our planet is relatively small. Nevertheless, if it does happen, the extent of the damage remains unclear.
That's because the force of its impact will be determined by aspects of its composition that are still unknown, and a more specific assessment of its size is also required, experts state.
.
The likelihood of impact remains extremely low, and the most probable outcome will be a near approach of a rock that will ultimately pass us by,' he stated.
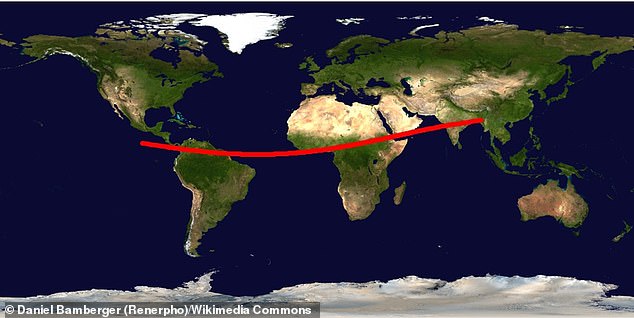
He commented that the current 'risk corridor,' or the geographical area where the asteroid is most likely to strike, spans from South America, crossing the Atlantic Ocean to sub-Saharan Africa.
There is a possibility that this risk corridor will change based on new observations and more precise orbital calculations.
looking for moving objects.
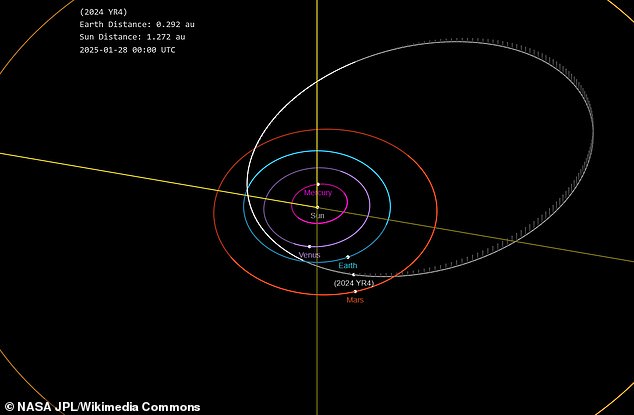
A telescope called ATLAS in Rio Hurtado, Chile, distinctly picked up the presence of a space rock on December 27, 2024, situated approximately 27 million miles away.
.
This space rock has been assigned a rating of three on the Torino impact hazard scale, a method for classifying potential Earth impact hazards.
A score of three indicates that asteroid 2024 WR4 deserves attention from astronomers since it will have a close encounter with Earth and it has a one percent or higher probability of impacting the planet.
However, there are still many uncertainties surrounding asteroid 2024 YR4, which makes it challenging to fully comprehend the potential risks posed by a potential direct impact on our planet.
"The size and composition of the asteroid, as well as its strike location, are critical factors in determining the extent of potential damage," Rankin explained.
"It's very challenging to define the size and composition due to the current orbital direction, which is moving away from us," he added.
Usually, the most effective method for estimating an asteroid's size is through the use of radar observations, as stated by Rankin.
This technique reflects radio waves or microwaves off an asteroid's surface and then analyses the reflections to determine its size.


Currently, astronomers are unable to use this method on 2024 YR4 due to its immense distance, but they may be able to conduct radar observations in 2028 when the asteroid is expected to pass approximately 5 million miles away from Earth, according to Rankin.
Until astronomers can directly observe the asteroid, they must use its absolute brightness, or magnitude, to make an approximate estimation of its size.
This calculation results in a rough diameter of 196 feet, although this is subject to a certain margin of error, primarily due to potential inaccuracies in the asteroid's surface reflectivity.
"If the asteroid has a darker surface, the number is too small; if it has a more reflective surface, the number is too high,' Rankin said.
The shininess of asteroids is influenced by their composition, and their composition also plays a significant role in how space rocks behave when they enter into Earth's atmosphere.
If asteroid 2024 YR4 is composed of stony material, it may produce a substantial air burst and fireball that reaches the ground, Rankin stated.
If made of iron, it would penetrate the atmosphere with ease and create a significant impact crater. Therefore, comprehending not only the orbit but also the composition and dimensions is of vital importance.
Now that 2024 YR4 has been pinpointed as a potential—but improbable—threat, the intense effort to gather as much information as possible about it has begun, with researchers attempting to acquire as much knowledge before 2032.
Read more