- Scientific research confirms that asteroid Bennu is composed of organic material, essential for the creation of life.
The "city-destroying" asteroid with a potential trajectory toward Earth has been captured in a new video, offering a first glimpse into what is yet to come.
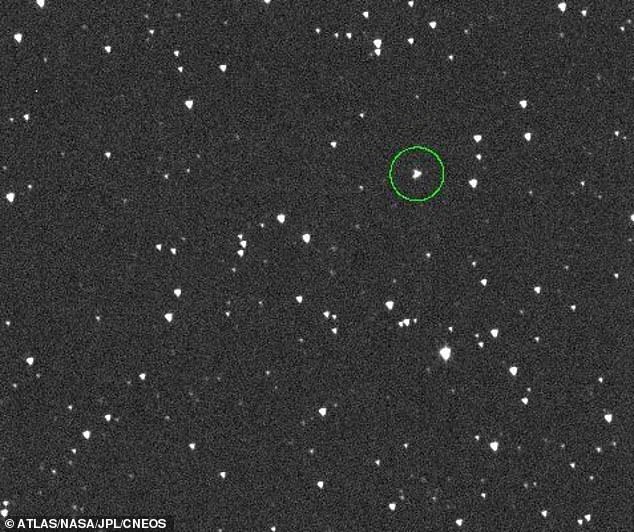
NASA has discovered the roughly 200-foot-wide space object, designated as asteroid 2024 YR4, located approximately 35 million miles from our planet.
The video showed the asteroid as a bright, glowing dot moving rapidly through the darkness of space, speckled with other luminous objects.
.
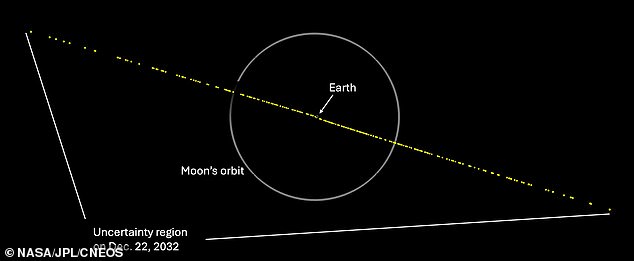
The initial detection enabled them to capture images of the space-rock's trajectory, depicting it hurtling through space as it follows an elliptical orbit around the sun.
The automated Sentry risk list that ranks known Near Earth Objects (NEOs) based on their likelihood of colliding with our planet.
"Typically, the initial orbit was only calculated accordingly, and the forecast uncertainties for 2032 were extremely large, meaning that the likelihood of the object having an exact collision course was very low," NASA stated.
'With each new observation, the path that C/2013 A1 is predicted to take has become more precise, and by 2032 it's expected to be confined to a relatively small area on a simplified map, with Earth steadily falling within that defined zone.'

This type of storm, especially if it occurs in a densely populated area such as a significant city like Tokyo or New York, can lead to severe consequences due to the high population density.
When it entered Earth's atmosphere in 1908, reportedly resulting in the deaths of three people.
It exploded in the sky above Siberia in a phenomenon known as an "air burst," and an explosion equivalent to detonating 50 million tons of TNT obliterated approximately 80 million trees over an area of 830 square miles of forest.
If comet 2024 YR4 were to enter Earth's atmosphere in 2024, it could potentially disintegrate or explode in the air, much like the Tunguska asteroid explosion.
"In the unlikely event that asteroid 2024 YR4 is on a collision course, the impact would occur within a potential impact corridor spanning the eastern Pacific Ocean, northern South America, the Atlantic Ocean, Africa, the Arabian Sea, and South Asia," NASA stated.
However, astronomers have also suggested that the object could potentially remain intact throughout its descent and collide with the ground, resulting in a massive crater and causing devastating effects on human settlements in the area.
Based on initial observations of the 2024 YR4 asteroid, scientists have identified its "risk corridor," or the geographical area where it is most likely to impact.
Furthermore, the estimated 2024 YR4's damage potential will depend on a more precise calculation of its size and specifics concerning its internal make-up and composition which experts currently lack information about.


As the asteroid draws nearer, astronomers will be able to conduct more detailed observations that can help them understand the precise size of 2024 YR4, its composition, and its internal structure.
Despite this, the likelihood that 2024 YR4 will impact our planet is minimal. Astronomers claim it is far more probable that this asteroid will safely bypass our planet in 2032.
But until that happens, the likelihood is expected to be "wobbly around a bit" as astronomers collect more observations that aid them in refining the asteroid's orbital path and trajectory, he said.
Here is the paraphrased text: 'This is the straightforward way scientific data measurements commonly unfold.'
Astronomers will closely monitor this space rock over the next eight years to gain a more precise understanding of its potential threat to our planet.
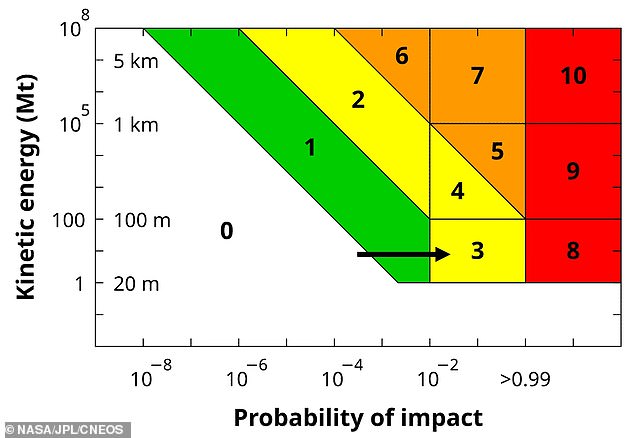
Currently, 2024 YR4 has been designated a three on the Torino impact risk scale, a method for assessing potential Earth impact hazards.
A score of three indicates the asteroid deserves attention from astronomers because it poses a risk of a close encounter with Earth and has a one percent or higher probability of impacting the planet.
This is a scale from zero to 10, with higher numbers showing a greater potential impact.
Most near-Earth objects never exceed a rating of two on the scale.
With 2024 YR4 now recognized as a potential, although unlikely, threat, the countdown begins to gather as much information about it as possible before 2032.
Read more